
Last updated on July 24th, 2022 at 08:04 am
Avenue Supermarts Ltd.- is it a crown of organized Retail?
Introduction
Avenue Supermarts Ltd (ASL) owns and operates D-Mart stores, an Indian chain of hypermarkets founded by Radhakishan Damani in the year 2002. It functions in the organized retail sector operating in a B2C (Business to Customer) model. D-mart attracts low and medium-income groups by providing branded premium quality products at a low cost. As of March 31, 2020, ASL has 214 stores with retail business area of 7.8 million sq. ft. across Maharashtra, Gujarat, Daman, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, NCR, Chhattisgarh, and Punjab.
Latest >>>Will the WEAK Q1 results, impact the stock in the long run?
Key Highlights
- Robust business model focussing on low operational costs.
- Virtually debt-free.
- Ownership based store operating model.
- Strong financial profile with EBITDA margins at 8.78% and an increase in PAT by 44.2% to Rs 1300.9 crores for FY 20.
- Superior RoCE of 23% and fixed asset turnover ratio of 4.1x.
- Strong liquidity, cash, and investments worth Rs 3261.8 crores in FY 20.
Future prospects
- The impact on profitability and margins in FY 21 is expected due to increased operational cost and reduced sales due to COVID-19.
- Faces competition from e-commerce players like Amazon, Big Basket to name a few among others having strong e- retail operations. However, D-Mart has taken initiatives like D-Mart on wheels to large housing complexes during the lockdown. Online grocery is now the fastest-growing segment in e-retail.
- Newly opened stores are growing at a fast pace benefiting from an established brand of D-Mart.
- Future expansion plans in Central and North India. The strategic expansion would lead to long-term benefits in the form of economies of scale, lower cost of sourcing from suppliers, and results in customer loyalty.
- D-Mart is increasing its share of private labels (D-Mart’s own brand) which in turn increases profitability, as their brands also get established in more geographies through expansion.
- The ability of D-Mart to realign with local consumer preferences.
- The strategy of maintaining cost efficiencies while offering the best customer value, D-Mart has continued to witness stable performance across financial and operational parameters, year-on-year.
Business profile
D-Mart has a robust business model which has made it the most profitable supermarket chain in India. It follows the model of low cost – low price similar to that of Walmart. They also follow a store ownership model resulting in owning almost all of its stores.
The product portfolio comprises of everyday use products categorized as Foods, Non-foods (FMCG), General Merchandise, and Apparel. Ongoing demand for the basic day to day goods creates demand throughout the year which eliminates the risk of demand fluctuations and provides stability to the business. Also, D-Mart has made the foray into digital space by opening D-Mart ready stores, thus competing with online grocery giants.
In FY 20 share of the revenue from the food category was 52.4%, FMCG products accounted for 20.29% and the rest 27.31% was from the general merchandise and apparel category (refer chart 1). Food and FMCG category earns 10-15% margins and general merchandise and apparel business have a margin of 20-25%.
It is also to be noted that the credibility of a retail company benefits with a rise in the share of private labels (D-Mart’s own brand) to overall sales as private labels tend to generate better profitability, than
branded products of other manufacturers. D-Mart has established its private label, Premium among large masses.
Chart 1

D-Mart has always focused on low cost, some of its low-cost drivers are :
- Purchase in wholesale directly from the manufacturer thus eliminating the middlemen cost.
- Availing discounts due to the policy of fast pay-outs to vendors.
- Low expenditure on the interior of stores and efficient space utilization.
- High volume sales result in bulk purchases which in turn help in getting volume discounts from manufacturers.
- Operations in self-owned stores lower its operational cost.
- Slotting fees charged by D-mart from manufacturers to keep their products on the shelf reduces its cost.
Financial Review
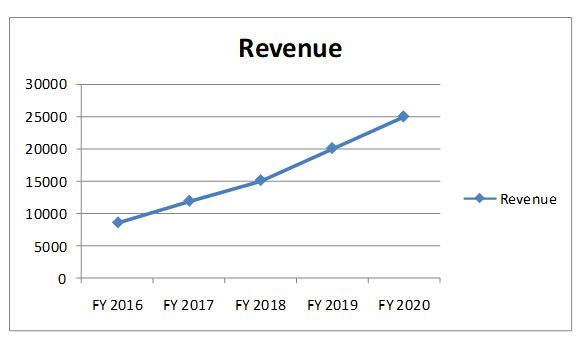
Total revenue has increased by 24% in FY 2020 to Rs 24930 crores from Rs 20052 crores (refer chart 2 for increasing trend of revenue). Gross profit margin is 8.78% in FY 2020 and it has remained in the range of 8%-9% in the last five financial years. Net profits have increased to Rs 1300.98 crores in FY 2020 from Rs 902.46 crores in FY 2019 (44.2% increase) and net profit margin is 5.22% for FY 2020.
D-mart has a very low debt to equity, just 0.03 times of equity in FY 2020. The interest coverage ratio is strong at 26.24times in FY 2020. It has not declared any dividend since the last five years indicating its growth plans.
Table 1 – Financials and Ratios (Amount in INR Crores)
[su_table]
| Particulars |
FY 2020 |
FY 2019 | FY 2018 | FY 2017 |
FY 2016 |
| Total revenue |
24930.19 |
20052.87 | 15102.52 | 11926.25 |
8601.7 |
| PAT |
1300.98 |
902.46 | 787.8 | 491.72 |
320.31 |
| EBITDA |
2188.3 |
1681.64 | 1422.14 | 1009.8 |
681.54 |
| Total Assets |
12076.45 |
7005.72 | 5648.37 | 5819.35 |
3101.55 |
| EBITDA margin |
8.78 |
8.39 | 9.42 | 8.47 |
7.92 |
| Net profit margin |
5.22 |
4.50 | 5.22 | 4.12 |
3.72 |
| Interest coverage ratio (times) |
26.24 |
31.12 | 21.21 | 7.23 |
6.38 |
[/su_table]
Chart 2
Valuation
ASL is one of the highly valued shares (market cap of 146779.27 crores) in the retail sector as well as among all the listed companies in India. The P/E ratio is 109 against the industry average of 70.83 in the retail sector signifying high expectations of shareholders from the share and future growth prospects in ASL. The price to book value is 13.18, being highest among its peers.
COVID- 19 Impact
FMCG companies have been hit by COVID- 19, however, the demand for household essentials has continued. Under the COVID scenario, except for the items under the grocery and FMCG category, D- mart has suspended the sale of shoes, apparel, and stationery items. Also, 50% of the stores remained closed based on directives by local authorities and footfall fell significantly during the lockdown period. D-mart started e-commerce home deliveries in bulk to large housing complexes in April but sales from these channels at present are insignificant.
D-Mart continues to face competition in the present scenario from E-commerce giants like Amazon, Big Basket, and others which offer doorstep groceries through their well-established network. The lockdown effect would be seen with lower EBITDA margins in the next one or two years due to reduced sales, lower footfall, higher sanitization cost of stores, and hardship allowance to frontline staff. The company continued to add larger stores with an average sq ft of 50000 (vs. average run rate 30000 sq ft.). Same-store sales (SSSG) growth dipped to 10.9% vs. 17.8% in FY19. SSSG for matured stores (>five years) slowed down whereas new stores are peaking at faster clips (even before they qualify for 24 months SSSG calculations).
Revenues will remain stable because major share comes from the food category but its margins may be lower in the next two years because the higher-margin business of general merchandise and apparels remains closed.
Peer Comparison
Some of the peers of D-Mart are Trent, Aditya Birla, Future Retail and V mart Retail but they differ in their size and scale of operations. Key information can be seen in the peer comparison table below.
[su_table]
| Peers (In Crores) |
Total Revenue |
Market cap | P/E | Book Value |
P/BV |
| Trent |
880.54 |
16668.81 | 107.78 | 70.3 |
6.67 |
| Aditya Birla |
1848.5 |
9268.03 | NA | 16.59 |
7.22 |
| Future retail |
5144.51 |
4597.88 | 6.5 | 71.19 |
1.19 |
| V mart retail |
333.45 |
2894.53 | 50.9 | 223.38 |
7.14 |
| Avenue Supermart |
24930.19 |
146779.27 | 108.89 | 171.9 |
13.18 |
[/su_table]
Future Outlook
ASL would continue to have positive sentiments due to its nature of business and operational advantages that differentiate it from its peers.
D-Mart’s share 52 weeks low is Rs 1280 and high is Rs 2560. It has reached a high level and even in the COVID scenario it went down to levels of Rs 1800 and again bounced back to Rs 2500 recently which indicates growth potential in the share over the long term horizon. It might prove to be a multi-bagger stock backed by its superior operating and financial profile.
Related Posts
- One MobiKwik Systems Limited, MobiKwik IPO - 14/10/2021
- Bharti Airtel Rights Issue- Should You Subscribe? - 07/10/2021
- How to Check your IPO Allotment status? - 28/09/2021
Disclaimer: The above content is for general info purpose only and does not constitute professional advice. The author/ website will not be liable for any inaccurate / incomplete information and any reliance you place on the content is strictly at your risk.
Follow us on Social Media by clicking below
Follow @financepost_in

Be the first to comment